 Hey guys, here’s a glossary of terms that are industry specific. For many of you these terms are common knowledge. For everyone else I hope this clears up any ambiguities you may have! I am going to update this list over time, here’s what we have for now. If you are looking for a definition on a term please let us know and we’ll list it for you:
Hey guys, here’s a glossary of terms that are industry specific. For many of you these terms are common knowledge. For everyone else I hope this clears up any ambiguities you may have! I am going to update this list over time, here’s what we have for now. If you are looking for a definition on a term please let us know and we’ll list it for you:
Abandons – People that visit your site, fill out the call to action box, but do not purchase. Direct Response marketers often use the user information from the abandons to retarget their message via email, phone, and direct mail. This tactic, when used correctly, will convert a number of those abandons into customers.
Above The Fold – When you first land on a website, “above the fold” refers to the part of the screen that you naturally see without having to scroll down. This is often the best place to place banners as everyone that lands on the page will have the banner right in front of their eyeballs.
Advertiser – An individual or company that has a direct response offer for sale. The advertiser pays for traffic to his website, whether direct from the traffic source or through an affiliate.
Affiliate/Publisher – Affiliates/Publishers are individuals/companies that push traffic to advertisers. They are compensated by a bounty, which often comes in the form of CPA, CPL, or CPS.
Backing Out – When an offer is profitable to the point where the campaign is working.
Bounty – The amount of money affiliates get for every lead they bring in on an offer.
Compliance – In Direct Response marketing, it’s important to pay close heed to FTC, Visa, International, and individual State regulations. These “rules” are referred to as “compliance.”
Conversion Rate: The ratio of visitors who convert casual content views or website visits into desired actions based on subtle or direct requests from marketers, advertisers, and content creators
Content Curation: The act of finding, grouping, organizing or sharing the best and most relevant content on a specific issue. It is important to offer original perspective and insight expected from an “industry expert”.
CPC (Cost Per Click) – You pay only when someone clicks on your ad. This cost varies depending on how competitive the keyword is that you’re targeting. Some keywords we bid on cost .50 per click. Other’s cost up to $20.
I’ve found that some of the more expensive keywords are worth paying for. Focus on targeting commercial intent keywords that give you the highest conversion rate. Then calculate your EPC and determine what your profit margins are.
You can calculate CPC by:
Total Cost Of Traffic / Total Number Of Clicks
CPM (Cost Per Thousand Impressions) – You pay for a set dollar amount for every 1,000 people that view your add, whether they buy or not. Most people buy their media on a CPM basis.
On some display networks, such as Google’s ad network, you have the option to pay per click. Hence your ad may receive a million impressions, but you only pay if someone clicks it.
Most display networks, such as Value Click and EngageBDR, charge on a CPM basis.
CTR (Click Through Rate) – The number of times someone clicks on your ad vs. the number of impressions. On CPC search engines, a higher CTR means a your ad will achieve a higher position at a lower cost. Your goal is to achieve the highest CTR possible.
You can calculate CTR by:
Clicks/Impressions x 100
i.e. (10 clicks / 1,000 impressions) x 100 = 1% CTR
CPA (Cost Per Acquisition) – This is the cost to you for every sale you generate. CPA is a great way to define your profit margins early on in a campaign. If you’re selling a product for $200.00 that has a 50% profit margin, then you know that anything below a CPA of $100 is profit. The lower the CPA, the higher the profit you pay.
I always try to negotiate good CPAs. Did you know that large ad networks will allow you to buy traffic on a CPA basis vs. a CPM basis? That’s right. If you have a good offer and solid budget, everything is negotiable.
CPS (Cost Per Sale) – The cost that it takes in advertising to generate a sale.
CLV (Customer Lifetime Value) – This is the average dollar amount each customer is worth. There are a number of factors to include, such as how many times did they reorder/get rebilled, how much are you earning from the data monetization per client, and how much business did they refer.
Crawling the web: Search engines send out algorithms throughout the entire internet. The point is to determine which sites should rank where.
Direct Response Offer – An online offer that has elicits a direct response from the consumer. Many pages have a strong call to action above the fold.
Double Opt-in: A user has subscribed for a newsletter or other email marketing messages by explicitly requesting it and confirming the email address to be her own. This is usually done by responding to a confirmation email sent to the email address in question.
EPC (Earning Per Click) – EPC shows how much money are you making every time someone clicks on your ad.
EPC is what most advertisers/affiliates base their earnings off of. In the past it was conversion rates. EPC is an indicator of conversion and is also an indicator of what the click is really worth.
Geo targeting: In geomarketing and internet marketing is the method of determining the geolocation of a website visitor and delivering different content to that visitor based on his or her location, such as country, region/state, city, metro code/zip code, organization, IP address, ISP or other criteria.
Impression: An “impression” is a single view of your ad. If 10 consumers view your ad, then you received 10 impressions.
Inbound Link: Inbound links send visitors to your web site from outside web pages. Generally, this is seen as a good thing. The greater the content on your site, the higher your inbound link rate will be.
Keyword Research: Researching identified keywords to determine which phrases will provide the most search traffic.
Inventory: The banner and contextual space available for advertisers on websites, along with the number of impressions available. Here is an example of inventory available on MSNBC.com:
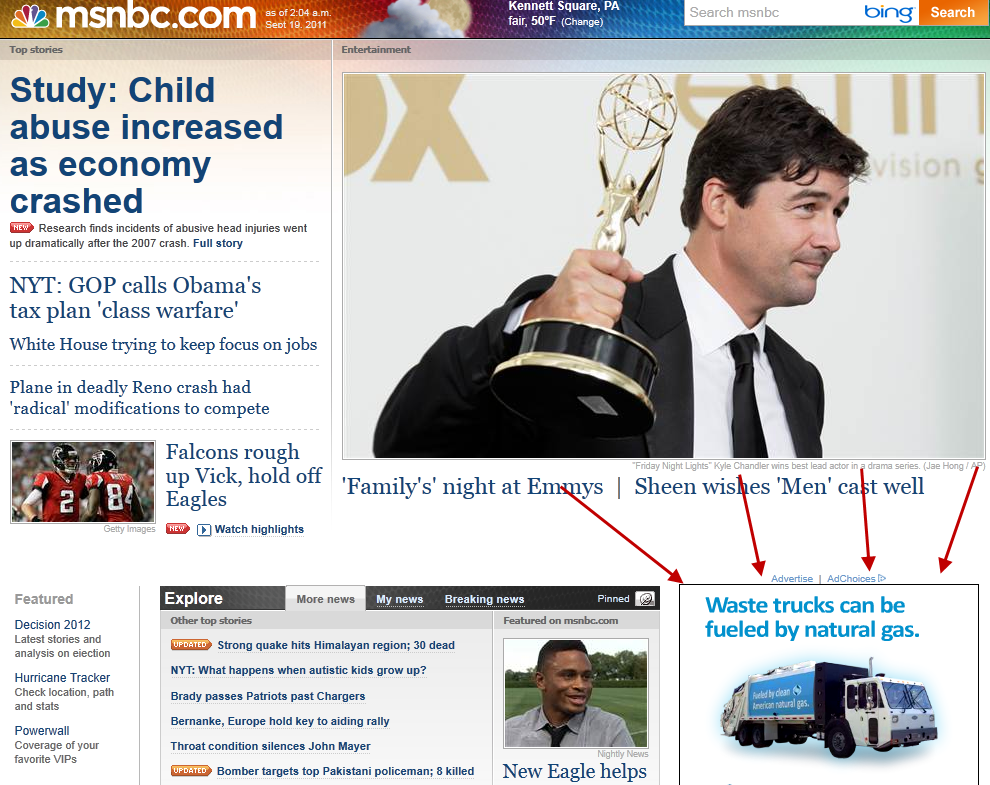
Lead – A lead is a new customer/contact that you brought to an offer. A lead can come in the form of a new customer that purchased a product or just a person that filled out a form.
Media Buy – This is where an advertiser/affiliate places a banner ad on a website. “Super Advertisers” (coined by Peter Nguyen) often buy ads on Quantcast top 1,000 websites. The more traffic the better. Other “Super Advertisers” often buy banner placements on thousands of niche sites at a time.
TIP: Buying in the members section of sites where customers paid via credit card has higher conversion rates vs. buying run-of the mill.
TIP: Buying remnant traffic is a good way to get traffic inexpensively.
Negative Keywords: In search engine advertising, “negative” keywords are used to filter words that are unrelated to the product or service being advertised but are in other categories that have the potential to generate impressions and clicks that are not relevant to the search query.
Offers: A product or service that’s for sale.
PageRank: A Google patented method for measuring page importance or relevance; ranges from 0 to 10, 10 being the best. PageRank is a Google link analysis algorithm and should not be mixed up with high rankings.
Paid Search Marketing: Paid search marketing is the process of gaining traffic by purchasing ads on search engines. It is sometimes referred to as CPC (cost-per-click) or PPC (pay-per-click) marketing, because most search ads are sold on a CPC / PPC basis.
Pop Under Advertisements: An ad that displays in a new browser window behind the current browser window.
The pop-under ad is the sneakier relative of the pop-up ad. While pop-up ads are often shown (and closed) instantly, pop-under ads linger behind the current browser window, appearing only after other windows have been closed.
PPV: PPV stands for pay-per-view, a type of ad campaign that is usually used with pop-ups, pop-unders and interstitial advertisements. Advertisers only have to pay when their ad window appears on a user’s browser. This allows for a more high impact advertising campaign.
You can advertise via PPV through sites like TrafficVance.com. TrafficVance.com has software that people download free and unbeknownst to them, adware is installed. From there TrafficVanace.com allows advertisers to deliver popup and popunders.
I am not a fan of PPV traffic as it is “interruptive marketing” and doesn’t work as well as other methods out there.
Presale Page: A presale page is a website that consumers are directed to after they click on an ad. This pages is used to create interest in DR offers and provides links to those offers. Presale pages often attempt to sell multiple items in one instance through a multiple step process, commonly known as “step 1″ and “step 2.”
Publisher (Ad Network Version): A website that sells advertising space in the form of banners or contextual.
Publisher (Affiliate Version): Affiliate marketers are often referred to as “pubs” or “publishers” because they “publish” offers, which means they advertiser offers.
Remnant Space – Unsold advertising space that is usually available at a discount. You can buy this space super cheap.
Search Engine Marketing (SEM):
The process of gaining traffic from or visibility on search engines. The phrase is also sometimes shortened to “search marketing.”
SEM is an umbrella term that covers two broad areas:
- Gaining traffic through free SEO efforts
- Gaining traffic through paid search advertising
Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
the process of getting traffic from the “free,” “organic,” “editorial” or “natural” listings on search engines. All major search engines such asGoogle, Yahoo and Bing have such results, where web pages and other content such as videos or local listings are shown and ranked based on what the search engine considers most relevant to users. Payment isn’t involved, as it is with paid search ads.
Search Engine Result Page (SERP): the listing of web pages returned by a search engine in response to a keyword query. The results normally include a list of web pages with titles, a link to the page, and a short description showing where the Keywords have matched content within the page. A SERP may refer to a single page of links returned, or to the set of all links returned for a search query.
Social Media Marketing:
Social media marketing refers to the process of gaining traffic or attention through social media sites.
Social media itself is a catch-all term for sites that may provide radically different social actions. For instance, Twitter is a social site designed to let people share short messages or “updates” with others. Facebook, in contrast is a full-blown social networking site that allows for sharing updates, photos, joining events and a variety of other activities.
Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Each advertisement must make a proposition to the consumer. Not just words, not just product puffery, not just show-window advertising. Each advertisement must say to each reader: “Buy this product, and you will get this specific benefit.”
Vertical: The category or type of affiliate campaign you are running. For example: dating services, vacations, health care, etc.











Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wished to say that I have really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts.
In any case I’ll be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write
again very soon!
I’d like to find out more? I’d like to find out
more details.
wholesale cheap Packers jerseys china Sizes Online
Reviews On cheap Bucks jersey